Example Delaunay Diagram
|
The following program generates a list
On the right you see a screenshot of the program showing the Delaunay
diagram. Clicking on the picture shows the |
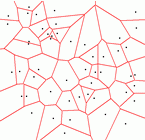 |
#include <LEDA/core/list.h>
#include <LEDA/geo/rat_point.h>
#include <LEDA/geo/rat_circle.h>
#include <LEDA/geo/random_rat_point.h>
#include <LEDA/graphics/window.h>
#include <LEDA/geo/geo_alg.h>
#include <LEDA/graph/edge_array.h>
using namespace leda;
int main()
{
list<rat_point> L;
random_points_in_square(50,100,L);
GRAPH<rat_circle,rat_point> G;
delaunay_voronoi_kind kind;
VORONOI(L,G);
kind=NEAREST;
//F_VORONOI(L,G); //Furthest Point Voronoi Diagram
//kind=FURTHEST;
if (Is_Voronoi_Diagram(G,kind))
std::cout << "G is a Voronoi Diagram" << std::endl;
else std::cout << "WARNING: G is no Voronoi Diagram!" << std::endl;
window W;
W.init(-110,110,-110);
W.open(); W.display();
W.set_node_width(2);
W.set_line_width(2);
std::cout << "Nodes of Voronoi diagram" << std::endl;
edge e;
forall_edges(e,G) {
point p=G[e].to_point();W.draw_filled_node(p);
}
W.read_mouse();
std::cout << "Edges of Voronoi diagram" << std::endl;
edge_array<bool> drawn(G,false);
forall_edges(e,G) {
if (drawn[e]) continue;
drawn[G.reversal(e)] = drawn[e] = true;
node v = source(e); node w = target(e);
if (G.outdeg(v) == 1 && G.outdeg(w) == 1) {
//special case: exactly two sites
rat_line l = p_bisector(G[v].point1(),G[v].point3());
W.draw_line(l.to_line(),red);
}
else if (G.outdeg(v) == 1) { //v at infinity
rat_point cw = G[w].center();
rat_vector vec = G[v].point3() - G[v].point1();
rat_point cv = cw + vec.rotate90();
W.draw_ray(cw.to_point(),cv.to_point(),red);
}
else if (G.outdeg(w) == 1) { //w at infinity
rat_point cv = G[v].center();
rat_vector vec = G[w].point3() - G[w].point1();
rat_point cw = cv + vec.rotate90();
W.draw_ray(cv.to_point(),cw.to_point(),red);
}
else { //both v and w proper nodes
rat_point cv = G[v].center();
rat_point cw = G[w].center();
W.draw_segment(cv.to_point(),cw.to_point(),red);
}
}
W.read_mouse();
W.screenshot("voronoi_diagram");
return 0;
}
See also:
Verification of Geometric Structures